우테코 - 톰캣 구현하기 미션 회고 (feat. 나도 톰캣 컨트리뷰터..?)
톰캣 구현하기 미션을 진행하면서 있었던 과정을 회고해보자

레벨 1, 2 때 미션을 하면서 느낀 점이 우선 구현(리팩터링을 약간 곁들인)을 하고 나서 추가시간을 들여 리팩터링을 하는 게 좋을 것 같다고 느꼈는데 이번 미션에 적용해 봄으로써 확실히 이게 내 개발 라이프 사이클인 것을 체감했다. 이전에는 구현을 하면서 동시에 리팩터링도 빡세게 하려다 보니 오히려 비즈니스 로직과 확장성이 머릿속에서 겹쳐서 뇌에 과부하가 와 시간이 굉장히 오래 걸렸다.
하지만, 이번에는 처음에 구현에 초점을 많이 맞추고 구현이 끝나고 난 뒤 추가적으로 리팩터링을 하였는데 시간적으로도 여유로웠고 관심사를 분리하니깐 머릿속으로도 여유로웠다. 한 가지 아쉬웠던 점은 이번에는 좀 극적으로 많이 구현에만 집중을 하고 리팩터링을 마지막에 몰아서 했었는데 그것보다는 구현을 하다가 리팩터링 할 때가 딱 보일 때, 그 적절한 때 하는 것이 베스트 인 것 같다. 물론 그 적절한 때를 찾기가 쉽지는 않겠지만 연습하다 보니 조금씩 감이 잡혀가는 것 같다.
요즘 설계에 관심이 많은데 다음 미션 때는 패키지 의존 쪽에 대해서도 고려를 해서 짜보면 좋을 것 같다. 다음 미션이 MVC 구현이라 요구사항이 빡세서 가능할진 모르겠지만… ㅋㅋ
자 이제 미션을 되돌아 보자~ 전체 코드는 해당 저장소에 있습니다.
톰캣을 구현해라

ㅖ…? 갑자기 톰캣을 구현하라고 하니깐 뭐부터 해야 될지 막막했다 ㅋㅋㅋ 나는 그동안 편리한 스프링 부트를 사용하였고, 그 안에 내장 톰캣이 알아서 돌아가고 있었기 때문에 막상 톰캣이 어떻게 돌아가는지는 생각해 본 적은 없는 것 같다. 그래서 톰캣이 어떻게 작동되는지부터 파악할 필요가 있었다.
1. 클라이언트 커넥션 수락
커넥터(Connector)는 클라이언트와의 통신을 처리하는데 서버의 특정 TCP 포트 번호에서 연결을 수신하고 요청 처리와 응답을 생성한다고 한다. 해당 구현 부분을 보면 다음과 같다.
private void connect() {
try {
process(serverSocket.accept());
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
대충 예측해 보면 serverSocket이 수락한다는 거 같은데 어떤 메서드일까?
Listens for a connection to be made to this socket and accepts it. The method blocks until a connection is made.
이 소켓에 연결이 이루어질 때까지 기다렸다가 연결을 수락한다고 나와 있다. 클라이언트가 요청을 보내면 기다리던 serverSocket이 연결을 수락하고, 클라이언트와 데이터를 주고받을 수 있게 된다.
2. 요청 메시지 수신
이제 연결을 했으니 클라이언트에게 받은 데이터를 읽어야겠죠?
@Override
public void process(final Socket connection) {
try (final var inputStream = connection.getInputStream();
final var outputStream = connection.getOutputStream()) {
...
} catch (IOException | UncheckedServletException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
InputStream을 통해 HTTP 요청 메시지를 네트워크로부터 읽는다. InputStream은 바이트 기반 입력 스트림 최상위 추상 클래스이고 XXXInputStream이라는 네이밍을 가진 하위 클래스들이 있다. 그리고 문자 단위 입력을 위한 최상위 입력 스트림 클래스인 Reader(ex.BufferedReadaer)를 통해 좀 더 편리하게 문자를 받아볼 수도 있다.
3. 요청 처리, 리소스 매핑과 접근, 응답 생성
클라이언트에게 받은 데이터로 어떤 요청(ex. “POST /login”)을 처리할지 어떤 리소스(ex. login.html)에 접근할지를 정할 수 있을 것이고 이를 기반으로 응답을 생성할 것이다.
@Override
public void process(final Socket connection) {
try (final var inputStream = connection.getInputStream();
final var outputStream = connection.getOutputStream()) {
HttpRequest httpRequest = HTTP_REQUEST_PARSER.convertToHttpRequest(inputStream);
HttpResponse httpResponse = new HttpResponse();
Controller controller = FRONT_CONTROLLER.handle(httpRequest);
controller.process(httpRequest, httpResponse);
...
} catch (IOException | UncheckedServletException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
위의 코드는 완성본이긴 하지만 슈도 코드를 살펴보자. InputStream을 통해 읽어들인 메시지를 기반으로 httpRequest를 생성하게 되고 해당 HttpRequest 안에는 HttpMethod, path, protocol 등… 요청 정보가 있다. 그리고 FRONT_CONTROLLER라는 클래스에서 해당 요청안의 path나 method를 보고 어떤 controller를 사용해야 될지 매핑을 해주고 해당 controller 로직을 처리한다.
해당 로직을 처리하게 되면 httpResponse 안에 각종 응답 정보(status code, header, body)들이 들어가게 되고 응답을 반환할 준비가 완료된다.
4. 응답 반환
응답을 반환할 준비가 되었으니 이제 응답을 반환할 수 있다.
@Override
public void process(final Socket connection) {
try (final var inputStream = connection.getInputStream();
final var outputStream = connection.getOutputStream()) {
HttpRequest httpRequest = HTTP_REQUEST_PARSER.convertToHttpRequest(inputStream);
HttpResponse httpResponse = new HttpResponse();
Controller controller = FRONT_CONTROLLER.handle(httpRequest);
controller.process(httpRequest, httpResponse);
outputStream.write(httpResponse.joinResponse().getBytes());
outputStream.flush();
} catch (IOException | UncheckedServletException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
httpReseponse.joinResponse()를 각종 응답 정보들을 String으로 Join 한 뒤 바이트로 변환해서 write 해주고 OutputStream을 통해 응답 헤더를 포함한 HTTP 응답 메시지를 생성한다. OutputStream은 바이트 기반 출력 스트림 최상위 추상 클래스이고 XXXOutputStream이라는 네이밍을 가진 하위 클래스들이 있다.
구현 과정
우선 요구사항은 다음과 같다. 요구사항
1단계 - HTTP 구현하기
2단계 - 로그인 구현하기
3단계 - 리팩토링
4단계 - 동시성 확장하기
처음에 구현에만 집중했기 때문에 메인 로직이 모두 Http11Processor 클래스에 모여있었다. 그래서 코드 줄 수를 보면 무려 260줄이… 첫 Http11Processor 코드
package org.apache.coyote.http11;
import nextstep.jwp.db.InMemoryUserRepository;
import nextstep.jwp.exception.UncheckedServletException;
import nextstep.jwp.exception.UserNotFoundException;
import nextstep.jwp.model.User;
import org.apache.coyote.Cookie;
import org.apache.coyote.HttpStatus;
import org.apache.coyote.Processor;
import org.apache.coyote.Sessions;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.URL;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Http11Processor implements Runnable, Processor {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Http11Processor.class);
private static final String STATIC_DIRECTORY = "static";
private static final String SPACE = " ";
private static final String QUERY_STRING_SEPARATOR = "\\?";
private static final String MULTIPLE_QUERY_STRING_SEPARATOR = "&";
private static final String KEY_VALUE_SEPARATOR = "=";
private static final String LINE_FEED = "\r\n";
private static final String HTML_SUFFIX = ".html";
private static final int PATH_INDEX = 1;
private static final int PROTOCOL_INDEX = 2;
private static List<String> STATIC_PATH = List.of(".css", ".js");
private final Socket connection;
public Http11Processor(final Socket connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("connect host: {}, port: {}", connection.getInetAddress(), connection.getPort());
process(connection);
}
@Override
public void process(final Socket connection) {
try (final var inputStream = connection.getInputStream();
final var outputStream = connection.getOutputStream()) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[2048];
inputStream.read(bytes);
final String request = new String(bytes);
final String response = createResponse(request);
outputStream.write(response.getBytes());
outputStream.flush();
} catch (IOException | UncheckedServletException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
private String createResponse(String request) throws IOException {
String path = getPath(request);
String method = getMethod(request);
String prevPath = path;
Cookie cookie = new Cookie();
Map<String, String> cookies = cookie.getCookies(request);
String jsessionid = cookies.get("JSESSIONID");
if (method.equals("GET")) {
path = processGetRequest(path, jsessionid);
} else if (method.equals("POST")) {
if (path.equals("/login")) {
path = processLogin(request);
} else if (path.equals("/register")) {
path = processRegister(request);
}
}
String status = getStatus(prevPath, path);
String protocol = getRequestElement(request, PROTOCOL_INDEX);
String contentType = getContentType(path);
String content = getContent(path);
String contentLength = "Content-Length: " + content.getBytes().length;
String response = protocol + SPACE + status + SPACE + LINE_FEED +
getJSessionId(request) + SPACE + LINE_FEED +
contentType + SPACE + LINE_FEED +
contentLength + SPACE + LINE_FEED +
getLocationIfRedirect(status, path) +
LINE_FEED +
content;
return response;
}
private String getJSessionId(String request) {
Cookie cookie = new Cookie();
Map<String, String> cookies = cookie.getCookies(request);
if (!cookies.containsKey("JSESSIONID")) {
return cookie.createCookie();
}
return "";
}
private String processLogin(String request) {
String path;
String[] splitRequestBody = getRequestBody(request);
String account = splitRequestBody[0].split(KEY_VALUE_SEPARATOR)[1];
String password = splitRequestBody[1].split(KEY_VALUE_SEPARATOR)[1];
try {
User user = InMemoryUserRepository.findByAccount(account).orElseThrow(UserNotFoundException::new);
addSession(request, user);
path = getRedirectPath(password, user);
log.info(user.toString());
} catch (UserNotFoundException e) {
path = "/401.html";
}
return path;
}
private void addSession(String request, User user) {
Cookie cookie = new Cookie();
Sessions sessions = new Sessions();
Map<String, String> cookies = cookie.getCookies(request);
String jsessionid = cookies.get("JSESSIONID");
sessions.add(jsessionid, user);
}
private static String[] getRequestBody(String request) {
String[] splitRequest = request.split(LINE_FEED);
String requestBody = splitRequest[splitRequest.length - 1].trim();
String[] splitRequestBody = requestBody.split(MULTIPLE_QUERY_STRING_SEPARATOR);
return splitRequestBody;
}
private static String processRegister(String request) {
String[] splitRequestBody = getRequestBody(request);
String account = splitRequestBody[0].split(KEY_VALUE_SEPARATOR)[1];
String email = splitRequestBody[1].split(KEY_VALUE_SEPARATOR)[1];
email = email.replace("%40", "@");
String password = splitRequestBody[2].split(KEY_VALUE_SEPARATOR)[1];
InMemoryUserRepository.save(new User(account, password, email));
return "/index.html";
}
private String getLocationIfRedirect(String status, String path) {
if (status.startsWith("302")) {
return "Location: " + path + SPACE + LINE_FEED;
}
return "";
}
private String getMethod(String request) {
return getRequestElement(request, 0);
}
private String getStatus(String prevPath, String path) {
if (!isSamePage(prevPath, path) && !prevPath.equals(path)) {
return HttpStatus.REDIRECT.getHttpStatusCode() + SPACE + HttpStatus.REDIRECT.getHttpStatusMessage();
}
return HttpStatus.OK.getHttpStatusCode() + SPACE + HttpStatus.OK.getHttpStatusMessage();
}
private static boolean isSamePage(String prevPath, String path) {
return (prevPath + HTML_SUFFIX).equals(path);
}
private String processGetRequest(String path, String jSessionId) {
if (isRequest(path)) {
if (haveQueryString(path)) {
path = processLogin(path);
return path;
}
if (path.equals("/login")) {
Sessions sessions = new Sessions();
if (sessions.isAlreadyLogin(jSessionId)) {
return "/index.html";
}
}
return path + HTML_SUFFIX;
}
return path;
}
private String processLogin(String path) {
String queryString = splitQueryString(path)[1];
String[] splitQueryString = queryString.split("&");
String account = splitQueryString[0].split(KEY_VALUE_SEPARATOR)[1];
String password = splitQueryString[1].split(KEY_VALUE_SEPARATOR)[1];
try {
User user = InMemoryUserRepository.findByAccount(account).orElseThrow(UserNotFoundException::new);
path = getRedirectPath(password, user);
log.info(user.toString());
return path;
} catch (UserNotFoundException e) {
return "/401.html";
}
}
private String getRedirectPath(String password, User user) {
String path;
if (user.checkPassword(password)) {
path = "/index.html";
} else {
path = "/401.html";
}
return path;
}
private boolean haveQueryString(String path) {
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(QUERY_STRING_SEPARATOR);
return pattern.matcher(path).find();
}
private String getContentType(String path) {
String contentType = "Content-Type: ";
if (isStaticPath(path)) {
return contentType + "text/css;charset=utf-8";
}
return contentType + "text/html;charset=utf-8";
}
private boolean isStaticPath(String path) {
for (String staticPath : STATIC_PATH) {
if (path.endsWith(staticPath)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private String getContent(String path) throws IOException {
if (path.equals("/")) {
return "Hello world!";
}
URL resource = getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(STATIC_DIRECTORY + path);
return new String(Files.readAllBytes(new File(resource.getFile()).toPath()));
}
private String getPath(String request) {
return getRequestElement(request, PATH_INDEX);
}
private boolean isRequest(String path) {
return !isStaticPath(path) && !path.endsWith(HTML_SUFFIX);
}
private String[] splitQueryString(String path) {
return path.split(QUERY_STRING_SEPARATOR);
}
private String getRequestElement(String request, int index) {
return request.split(SPACE + "|" + LINE_FEED)[index];
}
}
Oh My Goodness… 🤮🤮🤮 하나의 클래스에 책임과 역활이 너무 많다. 하나씩 분리해보자
HttpRequestParser, HttpRequest 분리
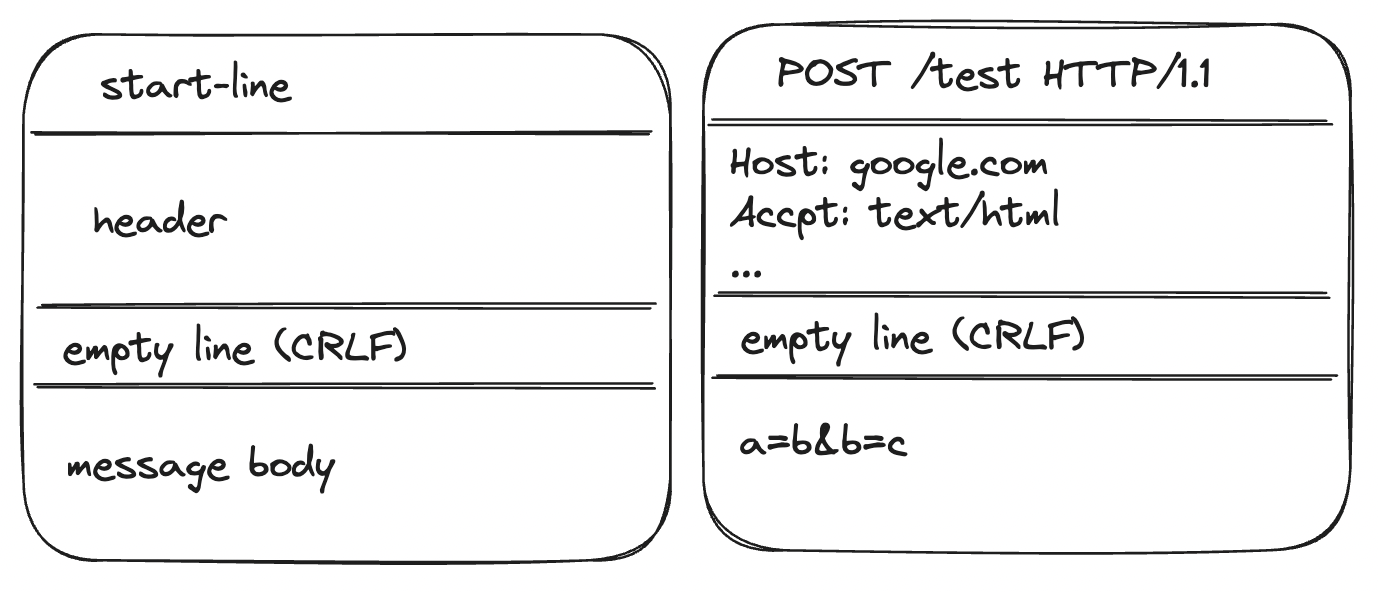
HTTP 요청 메시지를 보면 위와 같이 매우 복잡하게 되어있다. start-line, header, empty line, message body가 있고 또 그 안에서도 나뉜다.
그래서 구현할 때 제일 거슬렸던 게 읽는 부분이었다. 읽을 때마다 split을 하고 split에 몇 번째를 가져오고 또 그걸 split을 하고 ㅋㅋㅋ 그래서 이 부분을 가장 먼저 분리하자고 마음먹었다. 그렇게 다음과 같이 HttpRequestParser을 통해 데이터를 읽고 HttpRequest를 만들어 낼 수 있도록 분리하였다. HttpRequestParser, HttpRequest 코드
package org.apache.coyote.http;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class HttpRequestParser {
private static final int KEY_INDEX = 0;
private static final int VALUE_INDEX = 1;
public HttpRequest convertToHttpRequest(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
String firstLine = bufferedReader.readLine();
Map<String, String> header = readHeader(bufferedReader);
return new HttpRequest(new StartLine(firstLine), header, readMessageBody(bufferedReader, header));
}
private Map<String, String> readHeader(BufferedReader bufferedReader) throws IOException {
Map<String, String> header = new HashMap<>();
String line = bufferedReader.readLine();
while (line != null && !line.isBlank()) {
String[] split = line.split(":");
header.put(split[KEY_INDEX], split[VALUE_INDEX].strip());
line = bufferedReader.readLine();
}
return header;
}
private String readMessageBody(BufferedReader bufferedReader, Map<String, String> header) throws IOException {
String messageBody = "";
String contentLengthName = HttpHeader.CONTENT_LENGTH.getName();
if (header.containsKey(contentLengthName)) {
int contentLength = Integer.parseInt(header.get(contentLengthName));
char[] body = new char[contentLength];
bufferedReader.read(body, 0, contentLength);
messageBody = new String(body);
}
return messageBody;
}
}
package org.apache.coyote.http;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class HttpRequest {
private static final String KEY_VALUE_DELIMITER = "=";
private static final int KEY_INDEX = 0;
private static final int VALUE_INDEX = 1;
private StartLine startLine;
private Map<String, String> header;
private Map<String, String> cookies;
private String messageBody;
public HttpRequest(StartLine startLine, Map<String, String> header, String messageBody) {
this.startLine = startLine;
this.header = header;
cookies = findCookies();
this.messageBody = messageBody;
}
private Map<String, String> findCookies() {
return header.entrySet().stream()
.filter(entry -> entry.getKey().equals("Cookie"))
.map(entry -> entry.getValue().split("; "))
.flatMap(Arrays::stream)
.map(line -> line.split(KEY_VALUE_DELIMITER))
.collect(Collectors.toMap(line -> line[KEY_INDEX], line -> line[VALUE_INDEX]));
}
public boolean containsCookie(String key) {
return cookies.containsKey(key);
}
public String getCookie(String key) {
return cookies.get(key);
}
public void addHeader(String key, String value) {
header.put(key, value);
}
public HttpMethod getMethod() {
return startLine.getMethod();
}
public String getPath() {
return startLine.getPath();
}
public Map<String, String> getQueryStrings() {
return startLine.getQueryStrings();
}
public HttpProtocol getProtocol() {
return startLine.getProtocol();
}
public Map<String, String> getHeader() {
return header;
}
public String getMessageBody() {
return messageBody;
}
}
RequestBody를 읽을 때 무한루프에 빠지는 현상
HttpRequest를 좀 더 편리하게 읽기 위해 BufferedReader의 readLine()을 통해 읽었다. 하지만, 어느 부분에서 계속해서 무한 루프가 걸려서 브라우저가 계속 대기하는 현상이 일어났다. 해당 부분을 찾기 쉽지 않아 모든 곳에 디버깅을 걸어가며 확인한 결과 BufferedReader가 RequestBody 부분을 읽을 때 제대로 읽지 못하고 무한 루프가 발생하는 것을 발견하였다.
흠.. 수많은 삽질과 추론을 하다가 BufferedReader의 readLine()을 읽게 되었는데 다음과 같은 설명이 적혀있다.
Reads a line of text. A line is considered to be terminated by any one of a line feed (‘\n’), a carriage return (‘\r’), a carriage return followed immediately by a line feed, or by reaching the end-of-file (EOF).
텍스트 한 줄을 읽는데 줄 바꿈(‘\n’), 캐리지 리턴(‘\r’), 캐리지 리턴 다음 바로 줄 바꿈(‘\r\n’)이 오거나 EOF에 도달해야 종료된 것으로 간주한다는 것이다. 이걸 보고 HttpRequest의 내용을 쳐다봤다. start-line + CRLF + header + CRLF + message-body인데 message-body의 끝부분을 보면 위에서 해당하는 어떠한 것도 없다. 그래서 끝난지 모르고 계속해서 무한 루프를 돌고 있던 것이다! 🫢
그래서 RequestBody는 다음과 같이 read를 이용하여 contentLength 만큼 추가로 더 읽어주었다.
private String readMessageBody(BufferedReader bufferedReader, Map<String, String> header) throws IOException {
String messageBody = "";
String contentLengthName = HttpHeader.CONTENT_LENGTH.getName();
if (header.containsKey(contentLengthName)) {
int contentLength = Integer.parseInt(header.get(contentLengthName));
char[] body = new char[contentLength];
bufferedReader.read(body, 0, contentLength);
messageBody = new String(body);
}
return messageBody;
}
HttpResponseBuilder, HttpResponse 분리
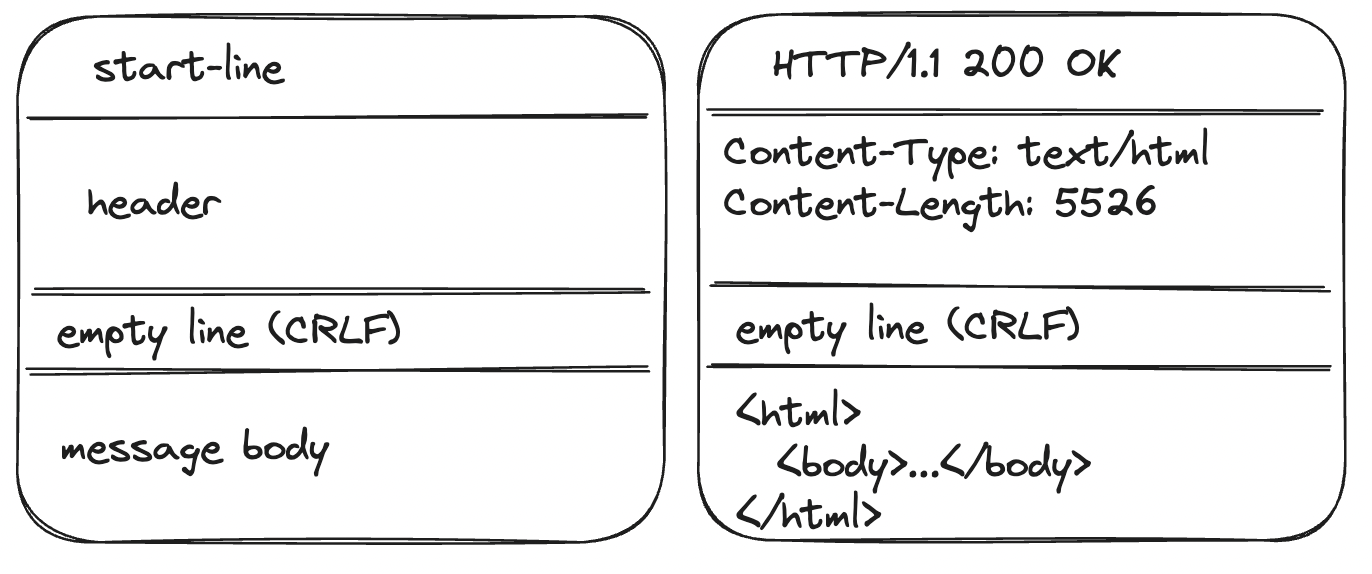
응답도 위와 같이 start-line, header, message body를 재구성 해줘야 되기 때문에 굉장히 중복된 부분이 많았다. 그래서 그다음 분리 대상으로 삼았고 HttpResponseBudiler를 이용해 HttpResponse를 생성할 수 있도록 분리하였다. 그리고 헤더를 추가할 때 기존의 헤더가 있으면 그 헤더에 추가적으로 추가할 수 있게 Header라는 추상 클래스를 만들고 콤마 구분자 헤더(ex. Cache-Control: no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate, max-age=0)와, 세미콜론 구분자 헤더(ex. Set-Cookie: a=b; c=d)를 분리했다. HttpResponseBuilder, HttpResponse, Header 코드
package org.apache.coyote.http;
import java.io.IOException;
public class HttpResponseBuilder {
private static final String LINE_FEED = "\r\n";
private static final String SPACE = " ";
private HttpResponseBuilder() {
}
public static void buildStaticFileOkResponse(HttpRequest httpRequest, HttpResponse httpResponse, String path) throws IOException {
try {
httpResponse.updateFileMessageBody(path);
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
buildStaticFileNotFoundResponse(httpRequest, httpResponse);
}
String status = joinStatus(HttpStatus.OK.getHttpStatusCode(), HttpStatus.OK.getHttpStatusMessage());
String protocol = httpRequest.getProtocol().getName();
String startLine = joinStartLine(status, protocol);
httpResponse.updateStartLine(startLine);
httpResponse.addHeader(HttpHeader.CONTENT_TYPE.getName(), ContentType.findType(path));
httpResponse.addHeader(HttpHeader.CONTENT_LENGTH.getName(), String.valueOf(httpResponse.getMessageBody().getBytes().length));
}
public static void buildStaticFileRedirectResponse(HttpRequest httpRequest, HttpResponse httpResponse, String redirectPath) throws IOException {
String status = joinStatus(HttpStatus.REDIRECT.getHttpStatusCode(), HttpStatus.REDIRECT.getHttpStatusMessage());
String protocol = httpRequest.getProtocol().getName();
String startLine = joinStartLine(status, protocol);
httpResponse.updateStartLine(startLine);
httpResponse.updateFileMessageBody(redirectPath);
httpResponse.addHeader(HttpHeader.LOCATION.getName(), redirectPath);
httpResponse.addHeader(HttpHeader.CONTENT_TYPE.getName(), ContentType.HTML.getType());
httpResponse.addHeader(HttpHeader.CONTENT_LENGTH.getName(), String.valueOf(httpResponse.getMessageBody().getBytes().length));
}
private static String joinStatus(String statusCode, String statusMessage) {
return statusCode + SPACE + statusMessage;
}
private static String joinStartLine(String status, String protocol) {
return protocol + SPACE + status + SPACE + LINE_FEED;
}
public static void buildStaticFileNotFoundResponse(HttpRequest httpRequest, HttpResponse httpResponse) throws IOException {
String status = joinStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.getHttpStatusCode(), HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.getHttpStatusMessage());
String protocol = httpRequest.getProtocol().getName();
String startLine = joinStartLine(status, protocol);
httpResponse.updateStartLine(startLine);
httpResponse.updateFileMessageBody("/404.html");
httpResponse.addHeader(HttpHeader.CONTENT_TYPE.getName(), ContentType.HTML.getType());
httpResponse.addHeader(HttpHeader.CONTENT_LENGTH.getName(), String.valueOf(httpResponse.getMessageBody().getBytes().length));
}
public static void buildCustomResponse(HttpRequest httpRequest, HttpResponse httpResponse, String content) {
String status = joinStatus(HttpStatus.OK.getHttpStatusCode(), HttpStatus.OK.getHttpStatusMessage());
String protocol = httpRequest.getProtocol().getName();
String startLine = joinStartLine(status, protocol);
httpResponse.updateStartLine(startLine);
httpResponse.updateMessageBody(content);
httpResponse.addHeader(HttpHeader.CONTENT_TYPE.getName(), ContentType.HTML.getType());
httpResponse.addHeader(HttpHeader.CONTENT_LENGTH.getName(), String.valueOf(httpResponse.getMessageBody().getBytes().length));
}
}
package org.apache.coyote.http;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class HttpResponse {
private static final String KEY_VALUE_DELIMITER = "=";
private static final String LINE_FEED = "\r\n";
private static final String SPACE = " ";
private static final String STATIC_DIRECTORY = "static";
private String startLine;
private Map<String, Header> headers = new HashMap<>();
private String messageBody;
public void updateStartLine(String startLine) {
this.startLine = startLine;
}
public void updateMessageBody(String messageBody) {
this.messageBody = messageBody;
}
public void updateFileMessageBody(String path) throws IOException {
URL resource = getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(STATIC_DIRECTORY + path);
messageBody = new String(Files.readAllBytes(new File(resource.getFile()).toPath()));
}
public void addHeader(String key, String value) {
Header header = headers.computeIfAbsent(key, ignore -> new CommaSeperatedHeader());
header.add(value);
}
public void addHeader(String key, List<String> values) {
Header header = headers.computeIfAbsent(key, ignore -> new CommaSeperatedHeader());
header.addAll(values);
}
public void addCookie(String key, String value) {
Header header = headers.computeIfAbsent(HttpHeader.COOKIE.getName(), ignore -> new SemicolonSeperatedHeader());
header.add(key + KEY_VALUE_DELIMITER + value);
}
public String joinResponse() {
return startLine +
joinCookie() +
joinHeaderWithoutCookie() +
LINE_FEED +
messageBody;
}
private String joinHeaderWithoutCookie() {
String headersWithoutCookie = this.headers.entrySet().stream()
.filter(entry -> !entry.getKey().equals(HttpHeader.COOKIE.getName()))
.map(entry -> entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue().getValues())
.reduce((header1, header2) -> header1 + SPACE + LINE_FEED + header2)
.orElse("");
return headersWithoutCookie + SPACE + LINE_FEED;
}
private String joinCookie() {
if (isStaticPath() || !headers.containsKey(HttpHeader.COOKIE.getName())) {
return "";
}
String cookieHeader = headers.get(HttpHeader.COOKIE.getName()).getValues();
String cookieHeaderResponse = Arrays.stream(cookieHeader.split("; "))
.map(line -> "Set-Cookie: " + line)
.reduce((cookie1, cookie2) -> cookie1 + SPACE + LINE_FEED + cookie2)
.orElse("");
return cookieHeaderResponse + SPACE + LINE_FEED;
}
private boolean isStaticPath() {
String contentType = headers.get(HttpHeader.CONTENT_TYPE.getName()).getValues();
return ContentType.isStaticFile(contentType);
}
public String getStartLine() {
return startLine;
}
public Map<String, Header> getHeaders() {
return headers;
}
public String getMessageBody() {
return messageBody;
}
}
package org.apache.coyote.http;
import java.util.Collection;
public abstract class Header {
protected final Collection<String> values;
protected Header(Collection<String> values) {
this.values = values;
}
public void add(String value) {
values.add(value);
}
public void addAll(Collection<String> values) {
this.values.addAll(values);
}
abstract String getValues();
}
package org.apache.coyote.http;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CommaSeperatedHeader extends Header {
protected CommaSeperatedHeader() {
super(new ArrayList<>());
}
@Override
String getValues() {
return String.join(", ", values);
}
}
package org.apache.coyote.http;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class SemicolonSeperatedHeader extends Header {
protected SemicolonSeperatedHeader() {
super(new ArrayList<>());
}
@Override
String getValues() {
return String.join("; ", values);
}
}
FrontController, Controller 분리
그렇게 request와 response 부분을 분리하니 앞뒤는 깔끔했지만 중간 부분이 굉장히 더러웠다. 특히 엄청나게 많은 분기문 + if 중첩문이 합쳐져서 가독성이 매우 구렸다. 이를 해결하기 위해서는 method와 path에 따라 해당 로직을 처리해주는 클래스를 매핑해주는 객체가 필요했다. 그리고 이 객체가 반환해 주는 클래스를 추상화한 객체까지.
그렇게 여러 분기의 Controller와 이 Controller를 공통화할 Controller Interface, 이 컨트롤러를 매핑해줄 객체가 생성되었다. 매핑해주는 객체 이름을 FrontController으로 지은 이유는 여러 Controller 앞에서 요청을 받아서 해당 Controller로 매핑해주기 때문이었다. FrontController, Controller 코드
package nextstep.jwp.presentation.handler;
import nextstep.jwp.presentation.Controller;
import nextstep.jwp.presentation.LoginController;
import nextstep.jwp.presentation.NotFoundController;
import nextstep.jwp.presentation.RegisterController;
import nextstep.jwp.presentation.RootController;
import nextstep.jwp.presentation.StaticController;
import org.apache.coyote.http.HttpRequest;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class FrontController {
private static final List<String> STATIC_PATH = List.of(".css", ".js", ".ico", ".html", ".svg");
private static final Controller NOT_FOUND_CONTROLLER = new NotFoundController();
private static final Controller STATIC_CONTROLLER = new StaticController();
private final Map<String, Controller> mappingControllers = new HashMap<>();
public FrontController() {
mappingControllers.put("/", new RootController());
mappingControllers.put("/login", new LoginController());
mappingControllers.put("/register", new RegisterController());
}
public Controller handle(HttpRequest httpRequest) {
String path = httpRequest.getPath();
if (isStaticPath(path)) {
return STATIC_CONTROLLER;
}
if (mappingControllers.containsKey(path)) {
return mappingControllers.get(path);
}
return NOT_FOUND_CONTROLLER;
}
private boolean isStaticPath(String path) {
return STATIC_PATH.stream().anyMatch(path::endsWith);
}
}
package nextstep.jwp.presentation;
import org.apache.coyote.http.HttpRequest;
import org.apache.coyote.http.HttpResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public interface Controller {
void process(HttpRequest httpRequest, HttpResponse httpResponse) throws IOException;
}
하나씩 분리한 결과
이렇게 하나하나 책임을 나눠주기 위해 분리한 결과 엄청나게 뚱뚱하던 Processor가 다음과 같이 성공적으로 다이어트를 하게 되었다.
package org.apache.coyote.http11;
import nextstep.jwp.exception.UncheckedServletException;
import nextstep.jwp.presentation.Controller;
import nextstep.jwp.presentation.handler.FrontController;
import org.apache.coyote.Processor;
import org.apache.coyote.http.HttpRequest;
import org.apache.coyote.http.HttpRequestParser;
import org.apache.coyote.http.HttpResponse;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Http11Processor implements Runnable, Processor {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Http11Processor.class);
private static final FrontController FRONT_CONTROLLER = new FrontController();
private static final HttpRequestParser HTTP_REQUEST_PARSER = new HttpRequestParser();
private final Socket connection;
public Http11Processor(final Socket connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("connect host: {}, port: {}", connection.getInetAddress(), connection.getPort());
process(connection);
}
@Override
public void process(final Socket connection) {
try (final var inputStream = connection.getInputStream();
final var outputStream = connection.getOutputStream()) {
HttpRequest httpRequest = HTTP_REQUEST_PARSER.convertToHttpRequest(inputStream);
HttpResponse httpResponse = new HttpResponse();
Controller controller = FRONT_CONTROLLER.handle(httpRequest);
controller.process(httpRequest, httpResponse);
outputStream.write(httpResponse.joinResponse().getBytes());
outputStream.flush();
} catch (IOException | UncheckedServletException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
현재 분리한 나의 구조는 다음과 같다.
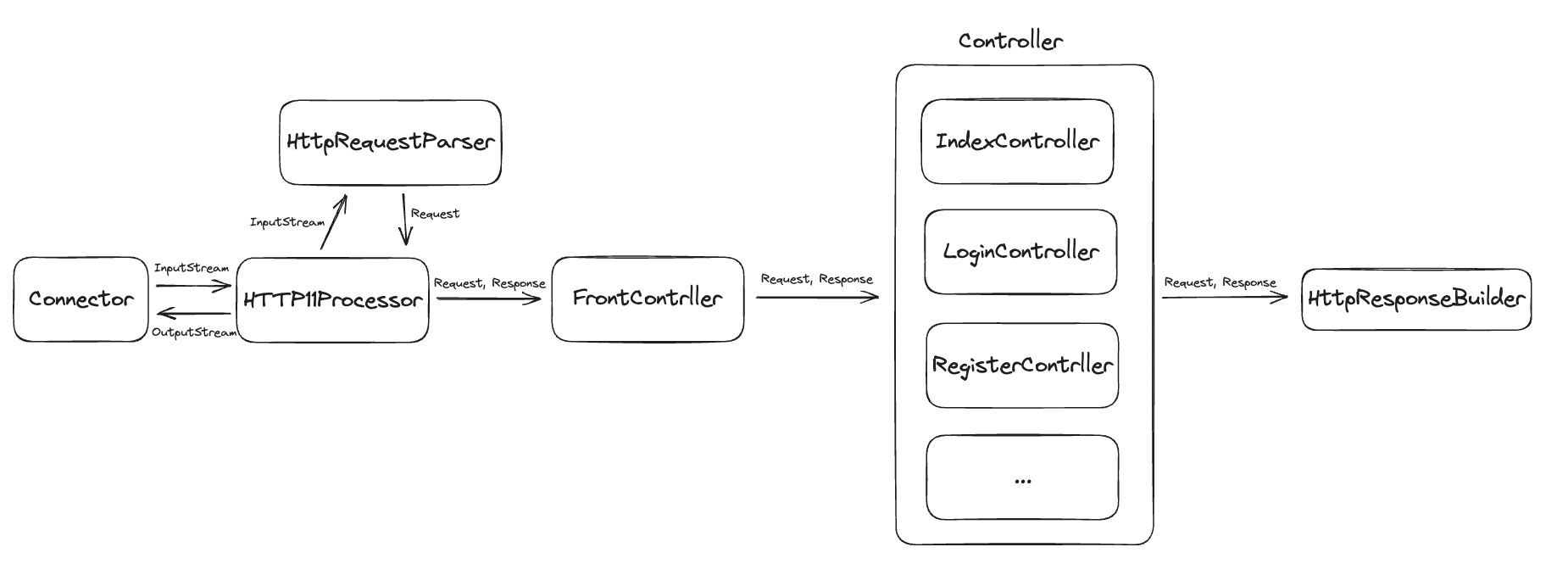
근데 이렇게 하나하나 분리해서 구현하다 보니깐 자연스럽게 Servlet의 구조와 비슷하게 되는 것 같았다. 이미 머리가 스프링에 너무 절여져서 그런가…? 뭐가 되었든 굉장히 의미있는 경험이었고 Tomcat과 좀 더 친해진 거 같다. 벌써부터 다음 미션인 MVC 구현하기가 매우 기대된다. 🤗
실제 톰캣은 어떻게 구현되어 있을까?
미션을 시작할 때 톰캣을 보지 않고 구현하고 나중에 실제 톰캣 코드와 비교해 보고 싶었다. 과연 실제 톰캣은 어떻게 구현되어 있을까? 내가 처리한 것들을 어떻게 효율적으로 처리하고 있는지, 엣지 케이스는 어떻게 처리해 주고 있는지 궁금했다.
우선 톰캣 패키지를 보면 Catalina, Coyote 패키지가 있다. Catalina 패키지는 서블릿 컨테이너 역할을 하며, Coyote 패키지는 톰캣에 TCP를 통한 프로토콜을 지원하는 역할을 한다.
처음에 요청이 들어오면 Connector를 통해 연결이 되고 Coyote 패키지의 Http11Processor 클래스 service() 메서드가 실행이 된다.
class Http11Processor {
@Override
public SocketState service(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper) throws IOException {
parse();
...
getAdapter().service(reuqest, reaponse);
...
}
}
요청으로 들어온 부분에 대해 파싱이 일어나고 그리고 getAdapter().service(request, response) 메서드를 호출한다. 해당 메서드를 호출하게 되면 Catalina 패키지에 있는 StandardWrapperValve 클래스의 invoke() 메서드가 실행되게 되고 다음과 같은 로직을 통해 알맞은 서블릿을 할당한다. StandardWrapperValve 클래스는 개별 서블릿 정의를 나타내는 Wrapper 인터페이스의 표준 구현이다.
class StandardWrapperValve {
// Allocate a servlet instance to process this request
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
...
try {
if (!unavailable) {
servlet = wrapper.allocate();
}
...
}
...
}
이렇게 서블릿을 할당하고 나면 해당 요청에 대한 filter chain을 호출한다. 해당 filter chain을 호출했을 때 다음에 호출할 필터가 있으면 계속해서 호출하며 작업을 처리하고 없으면 할당된 servlet의 service() 메서드를 실행하며 마무리한다. 그렇게 서블릿의 해당 로직을 처리하고 나서 응답을 반환하면 끝이 난다.
// Call the filter chain for this request
// NOTE: This also calls the servlet's service() method
Container container = this.container;
try {
if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) {
// Swallow output if needed
if (context.getSwallowOutput()) {
try {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
} else {
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
}
} finally {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
context.getLogger().info(log);
}
}
} else {
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
} else {
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
}
}
}
}
...
해당 과정을 간단하게 그림으로 나타내면 다음과 같다.
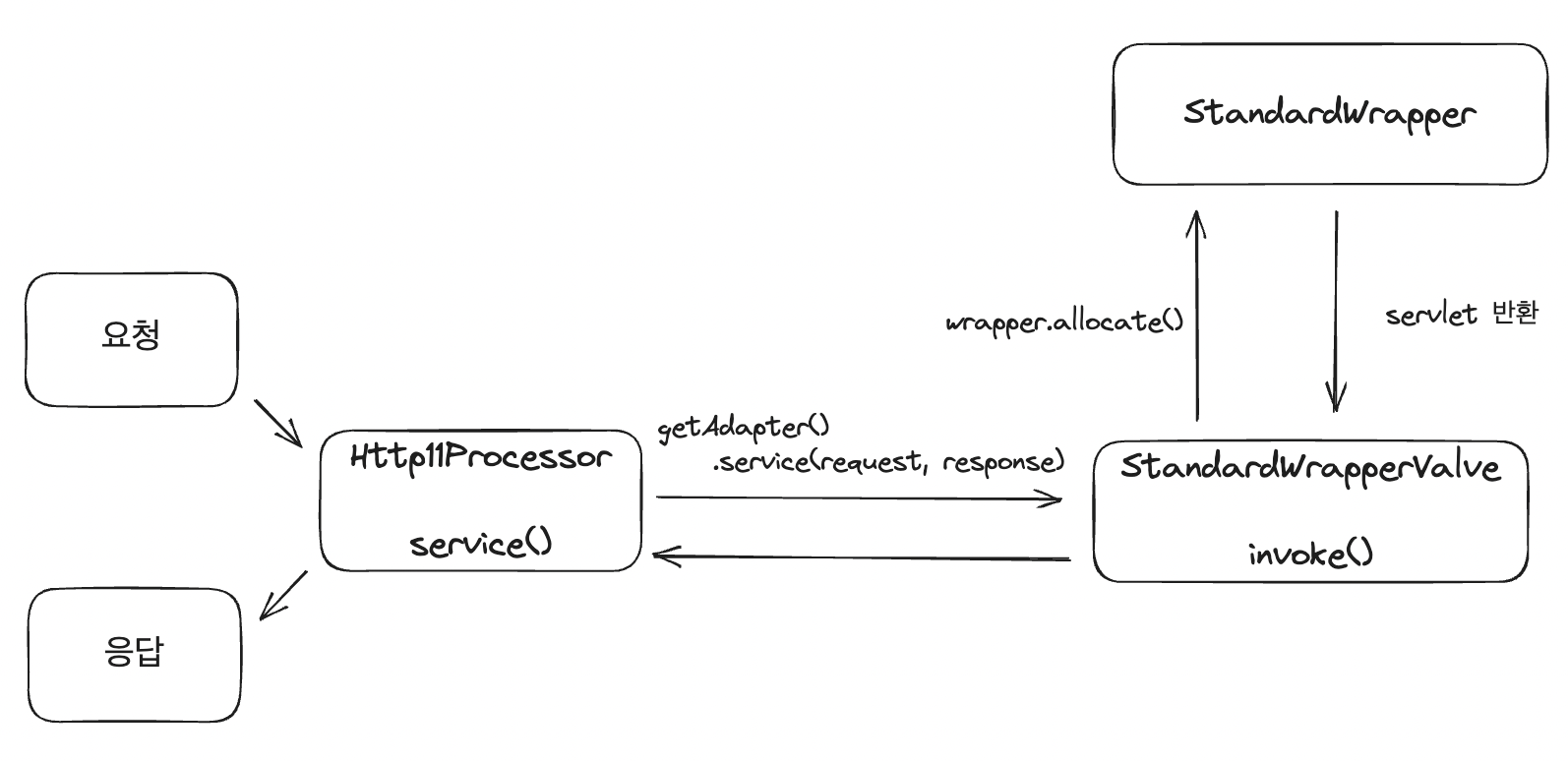
실제 구현되어 있는 톰캣과 흐름을 비교해 보면 비슷한 걸 확인할 수 있다. 근데 실제 톰캣 코드를 보다 보면 코드가 굉장히 길고 지저분한 걸 볼 수 있다. 대형 오픈소스 프로젝트니 어쩔 수 없겠지만 과정을 하나하나 추적하며 직접 찾아보는 게 너무 힘들었다ㅜㅜ 내가 FrontController라고 지은 객체는 톰캣에서는 Container(참고로, StandardWrapper가 Container 인터페이스를 implements 하고 있다) 와 Controller는 Servlet과 대칭되고 있는걸 확인할 수 있었다. 나는 이미 스프링에 머리 절여진 것 확인 🫠
톰캣 컨트리뷰트
코드를 분석 하는데 솔직히 말하면 코드가 정말 가독성이 좋지 않아 보기 힘들었다. 이미 오픈소스 프로젝트를 참여하고 있어서 오픈 소스 코드나 문화에 대해 익숙했기 때문에 톰캣 오픈소스도 기여해 볼 수 있지 않을까 생각했다.
그래서 이전에 보다가 조금 불편한 부분인 상수 컨벤션 불일치와 스위치문에 매직 넘버 사용 부분을 리팩터링 해 PR을 제출했다.
상수 컨벤션을 변경하면 3rd-party와 통합이 중단될 위험성도 있기 때문에 정말 타당한 이유가 없는 한은 변경하고 싶지 않다고 하여 상수 컨벤션 부분은 롤백 하였다. 하지만, 매직 넘버 부분은 받아들여져 결국 Merge가 되었다! 물론 오픈소스에 처음으로 기여한 것은 아니라 미친 듯이 설렌 건 아니지만 그래도 숨길 수 없는 입꼬리.. 🫢
참고:
*틀린 부분이 있으면 언제든지 말씀해 주시면 공부해서 수정하겠습니다.
